 BIO-MONITORS
BIO-MONITORS
- Micronutrient Testing assesses the intracellular requirements of micronutrients that play an
important role in overall health and wellness of your patients. Micronutrient tests measure
the biochemical function of vitamins, minerals, amino acids and antioxidants within
lymphocytes, providing a powerful clinical assessment tool for your practice.
- Deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, amino acids and antioxidants
are associated with the chronic degenerative disease processes such
as cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and
osteoporosis.
- Spectracell’s patented technology assesses long-term
intracellular requirements using each patient’s lymphocytes.
Under a variety of nutrient depletion conditions, the growth response
of these cells is measured to mitogenic stimulation. This determines
functional intracellular deficiencies, which are not detected by standard
serum tests.
- For individuals with deficiencies, consider repletion
with supplements and nutrients found in recommended
foods.
- Increased thromboxane production may lead to increased risk for heart attack and stroke.
- AspirinWorks® is an enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) to determine
levels of 11 – dehydrothromboxane B2 (11 - dhTXB2) in urine which aids
in the quantitative detection of aspirin effect in apparently healthy
individuals post ingestion.
- High levels of 11 - dhTXB2 are associated
with increased risk of heart attack and cardiac death
in aspirin-treated patients.
- Hyperlipidaemia is associated with diminished
response to aspirin.
- 11 – dhTXB2 levels demonstrate
a dose-related effect of aspirin treatment and have
been shown to correlate with the Framingham Risk Score.
- For individuals
on aspirin with abnormal 11-Dehydrothromboxane-B2
levels, consider adding omega-3 fatty acids or increasing the aspirin
dose to improve antiplatelet function if no contraindications for aspirin
therapy.
- Assess risk for pre-diabetes, diabetes.
- Creatine Kinase (CK) measures both acute and chronic injury to myocardial
cells.
- Blood levels of creatine kinase rise when heart cells or other
muscle cells are injured.
- Statins, especially when
combined with other lipid altering medications, can
damage muscles and increase creatine kinase levels.
- Measure creatine
kinase if acute signs of a heart attack or chest
pain occur and monitor levels for chronic injury combined with other
inflammatory markers.
- Repeat test if acute or chronic signs or symptoms
(i.e., sorness, fatigue, chest pain, dark color urine)
of muscle damage persist.
- Individuals with subclinical or clinical hypothyroidism are at higher
risk for heart failure and coronary artery disease.
- In subclinical hypothyroidism, the thyroid is not making enough thyroid
hormone, so TSH is increased to stimulate the thyroid resulting in
high TSH levels and normal thyroid function.
- Individuals with high
TSH may have a harder time losing weight and will
often exhibit lipid abnormalities. Test RMR, lipids, and treat thyroid
levels.
- Individuals with low TSH, especially if taking thyroid supplements,
are at risk for arrhythmias.
- Repeat 6 weeks after
initiating or changing therapy and then every 6 months.
- This panel includes 8 standard tests used to assess and monitor a patient’s fluid and electrolyte status,
kidney function, blood sugar levels, and response to various medications and other medical therapies.
- Abnormal values may indicate health issues like heart or kidney
disease.
- Repeat abnormal values monthly until underlying cause is
diagnosed.
- Abnormal hepatic enzyme levels may indicate liver damage.
- The liver stores and metabolizes foods and medications. Weight gain
and insulin resistance can increase the storage of triglycerides in
liver tissue, altering liver function.
- Medications are metabolized
by the liver and may alter liver function.
- Test hepatic functions
prior to initiation of of anti-lipemic medications
to get a baseline reading, 6 weeks after starting therapy, or if symptoms
develop.
- The CBC gives information about the kinds and numbers of cells
in the blood which can identify anemia, infections and other stresses
on the body.
- WBCs are released in response to injury or stress causing
inflammation. When combined with elevated platelets,
endothelial dysfunction can occur.
- Abnormal results can be a result
of acute or chronic disease processes. Identify underlying
causes.
- Combined with other labs, CBC can guide medication and lifestyle
therapy.
- Repeat abnormal values as needed until
treatment goal is met, then at least annually.
MICRONUTRIENT TESTS ASSOCIATED WITH METABOLIC CHARACTERIZATION
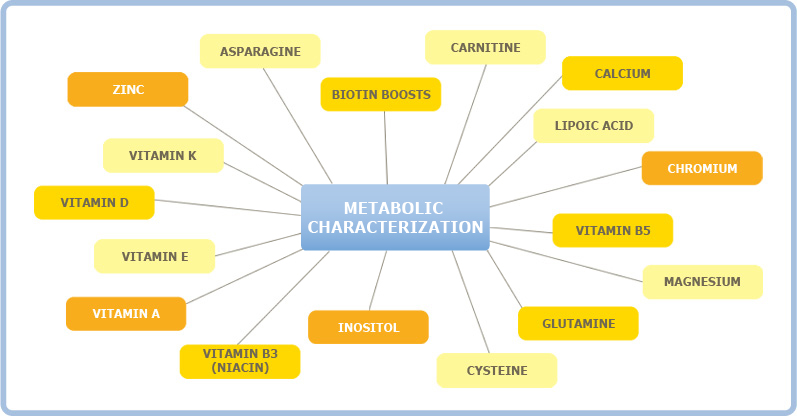
Asparagine
This amino acid increases insulin sensitivity which helps the body
store energy in muscle instead of storing it as body fat.
Biotin Boosts
metabolism by improving glycemic control (stabilizes blood sugar)
and lowering insulin, a hormone that promotes fat formation.
Carnitine
Carries fatty acids into the cell so they can be burned for fuel;
Helps reduce visceral adiposity (belly fat)
Calcium
Inhibits the formation of fat cells; Also helps oxidize (burn) fat cells.
Lipoic Acid
Improves glucose uptake into cells, which helps a person burn
carbohydrates more efficiently.
Chromium
Makes the body more sensitive to insulin, helping to reduce body
fat and increase lean muscle.
Vitamin B5
Taking B5 lowers body weight by activating lipoprotein lipase, an
enzyme that burns fat cells. One study liked B5 supplementation
to less hunger when dieting.
Magnesium
Low magnesium in cells impairs a person’s ability to use glucose
for fuel, instead storing it as fat; Correcting a magnesium deficiency
stimulates metabolism by increasing insulin sensitivity. Magnesium
may also inhibit fat absorption.
Glutamine
Reduces fat mass by improving glucose uptake into muscle.
Cysteine
Supplementation with this antioxidant reduced body fat in obese
patients.
Inositol
Supplementation may increase adiponectin levels.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Treatment with B3 increases adiponectin, a weight-loss hormone
secreted by fat cells; Niacin-bound chromium supplements helped
reduced body weight in clinical trials.
Vitamin A
Enhances expression of genes that reduce a person’s tendency to
store food as fat; reduces the size of fat cells.
Vitamin E
Inhibits pre-fat cells from changing into mature fat cells, thus
reducing body fat.
Vitamin D
Deficiency strongly linked to poor metabolism of carbohydrates;
Genes that are regulated by vitamin D may alter the way fat cells
form in some people.
Vitamin K
Poor vitamin K status linked to excess fat tissue; vitamin K helps
metabolize sugars.
Zinc
Deficiency of zinc reduces leptin, a beneficial hormone that
regulates appetites, which is reversed by zinc repletion
 PHYSICAL DIAGNOSTICS (PDxs)
PHYSICAL DIAGNOSTICS (PDxs)
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for dyslipidemia, hypertension, & insulin resistance.
- RMR accurately assesses an individual’s current caloric needs for
resting body functions including breathing, circulation, & digestion based on oxygen consumption.
- Exercise and lifestyle are considered with the current RMR to give
an estimate or caloric budget, aiding in weight management.
- RMR testing is recommended for individuals needing
to lose weight, struggling to lose weight, or at
risk for insulin resistance and hypertension.
- Repeat RMR after significant
weight or muscle changes as indicated through body
composition testing.

![]() BIO-MONITORS
BIO-MONITORS

![]() PHYSICAL DIAGNOSTICS (PDxs)
PHYSICAL DIAGNOSTICS (PDxs)
